Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems:
a) Non SEDDS/SMEDDS systems:
SEDDS/SMEDDS is not the universal answer for all solubility/bioavailability challenges, especially when:
- 1. Drug presents a very low Papp
- 2. Drug belongs to BCS Class IV
- 3. Active transport identified
- 4. Drug is sensitive to oxidation
Case study 3: In the following case study of an NCE-Drug A with:
- – MW ~ 400
- – cLog P > 8
- – Insoluble
The following had to be considered:
Is the digestion process likely to increase solubility?
- – Reservoir effect in LCLPs and MCLP.
Fig 7: Solutions in LCTs and MCTs with proven acceptable stability.
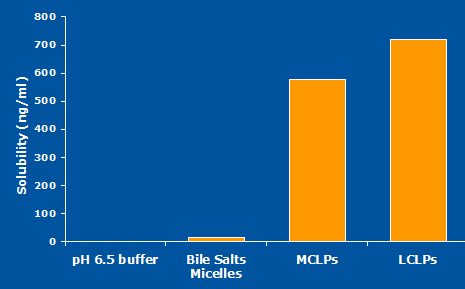
Fig 8: pK study in rats showing the potential for a LCT-based formulation.
Conclusion: Thus a drug substance suspension in LCTs was developed.
- • 45% drug load reached
- • Utilized milled drug substance
– Bet on the LCLPs "reservoir" potential - • The selected formulation was stable for 18 months.
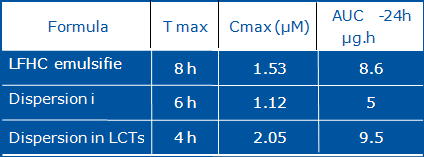
Fig 9: Reference data on Progesterone Solubility.
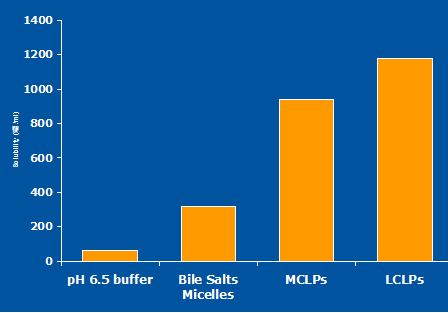
Table III: Reference pK data on progesterone formulations.
| Formulation | Cmax (ng/ml) Mean ± SD |
Tmax (h) Mean ± SD |
| Plain Milled Progesterone |
9,6 ± 2,5 | 4,0 ± 0,5 |
| Micronised Progesterone |
13,2 ± 2,4 | 3,2 ± 0,4 |
| Plain Milled Progesterone in Oil |
11,3 ± 3,0 | 4,0 ± 0,5 |
| Micronised Progesterone in Oil |
30,3 ± 7,0 | 2,0 ± 0,3 |
b) Lipid-Based Formulations for Solubility and Bioavailability Enhancement
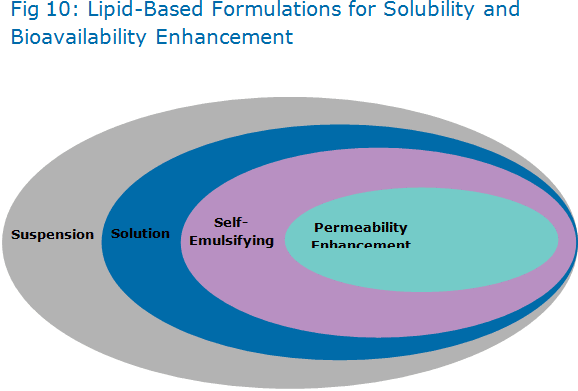
1. Suspension Formulations
Example: Prometrium® Softgels 100, 200 mg (progesterone)
2. Lipid-Based Solution Formulations
Example: Avodart® Softgels 0.5 mg (dutasteride)
c) Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS) Formulation of Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems
- • Lipid-Based "Preconcentrate" of Solubilised Drug
- • Typical Composition
— Lipid excipients
— Surfactants (hydrophilic, high HLB)
— Co-surfactants (lipophilic, low HLB)
— Co-solvents (ethanol)
Desired Characteristics Upon Dilution With the G.I. Fluids
- • Spontaneous Formation of Micro/Nanoemulsion
- • Drug Stays in Solution and Does Not Precipitate
Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems
Example: Cyclosporin A (the Neoral® Story)
Initially introduced as a Lipid-based Formulation in a Softgel - Sandimmune®
Reformulated as a Microemulsion Preconcentrate in a Softgel - Neoral®
- — Rapid gastric dispersion due to self-emulsifying properties
- — Maintain drug in solution using a solvent system which prevents precipitation
- — High drug concentration at the site of absorption
Neoral® is less affected by food intake
d) SMEDDS;
Example: SMEDDS system increased the bioavailability of CoQ10 (Ref 23).
e) Lipid-based Formulations for Permeability and Bioavailability Enhancement Permeability Enhancement
- • Passive transport through enterocytes
- • Passive transport around enterocytes (tight junctions)
- • Enterocyte-based active transport and metabolic processes (P-gp, CYP3A4, lipoproteins) Bioavailability Enhancement – Alternate Absorption Routes
- • Lymphatic transport
LBDS for Permeability Enhancement
Example: Saquinavir with Cremophor EL®
Saquinavir (a P-gp substrate) oral bioavailability was significantly increased when co-administered with Cremophor EL .
f) Film Coated Softgels for the Targeted Delivery of Poorly Soluble, Poorly Permeable Drugs
- • Post-gastric (targeted) drug delivery
- • Protection of acid-labile drugs from gastric fluids
- • Reduced local gastric side effects
- • Potential for enhanced drug absorption
— Rapid release of fill contents at targeted site of delivery following dissolution of film coat
— High local concentrations of API and permeation enhancers
Table V: Fill Formulation
| Ingredient |
| Active |
| Mono/Diglycerides of Capryl/Capric Acid |
| Caprylocapryl Macrogol Glycerides |
| Polysorbate 80 |
Table VI: Film Coat Formulation
| Ingredient |
| Eudragit® L30D 55 Dispersion |
| PEG 400 |
| Talc |
| Simethicone Emulsion |
| Purified Water |
12% Weight Gain
Table VII: In-vitro Disintegration (min)
| USP <701> |
T=0 | T=3 mon | T=6 mon | T=9 mon | T=12 mon |
| SGF, n=6 |
No evidence of disintegration | No evidence of disintegration | No evidence of disintegration | No evidence of disintegration | No evidence of disintegration |
| SIF, n=6 |
26 – 28 | 22 – 26 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 29 | 23 – 25 |

Fig 11: Disintegration in SGF Fig 12: Disintegration in SIF
g) Nutritional products/vitamin supplements can also be delivered in an enhanced bioavailable form as liquid in stickpacks .